
About Blockchain
The demand for blockchain developers and engineers keeps on increasing without pause. According to research done by management consulting firm, Janco Associates, the median salary for a blockchain developer is now as much as $127,000. Check that comprehensive list of 29 advanced blockchain interview questions and answers before your next blockchain interview.
Interview Questions & Answers
What is blockchain?
Blockchain is a secure distributed ledger (data structure or database) that maintains a continuously growing list of ordered records, called “blocks”, that are linked using cryptography. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data.
By design, a blockchain is resistant to modification of the data. It is “an open, distributed ledger that can record transactions between two parties efficiently and in a verifiable and permanent way”.
Once recorded, the data in any given block cannot be altered retroactively without alteration of all subsequent blocks, which requires consensus of the network majority.
Explain the common structure of blockchains
Blockchains are composed of three core parts:
- Block: A list of transactions recorded into a ledger over a given period. The size, period, and triggering event for blocks is different for every blockchain.
- Chain: A hash that links one block to another, mathematically “chaining” them together.
- Network: The network is composed of “full nodes.” Think of them as the computer running an algorithm that is securing the network. Each node contains a complete record of all the transactions that were ever recorded in that blockchain.
What is deterministic behavior?
If A + B = C, then no matter what the circumstances, A+B will always be equal to C. That is called deterministic behavior.
Hash functions are deterministic, meaning A’s hash will always be H(A).
What is proof-of-work?
A proof of work is a piece of data which is difficult (costly, time-consuming) to produce but easy for others to verify and which satisfies certain requirements. Producing a proof of work can be a random process with low probability so that a lot of trial and error is required on average before a valid proof of work is generated. Difficulty is a measure of how difficult it is to find a hash below a given target.
What is the Genesis Block?
The first block in any blockchain is termed the genesis block. If you start at any block and follow the chain backwards chronologically, you will arrive at the genesis block. The genesis block is statically encoded within the client software, that it cannot be changed. Every node can identify the genesis block’s hash and structure, the fixed time of creation, and the single transactions within. Thus every node has a secure “root” from which is possible to build a trusted blockchain on.
What is the blockchain data structure?
Basically the blockchain data structure is explained as a back-linked record of blocks of transactions, which is ordered. It can be saved as a file or in a plain database. Each block can be recognized by a hash, created utilizing the SHA256 cryptographic hash algorithm on the header of the block. Each block mentions a former block, also identified as the parent block, in the “previous block hash” field, in the block header.
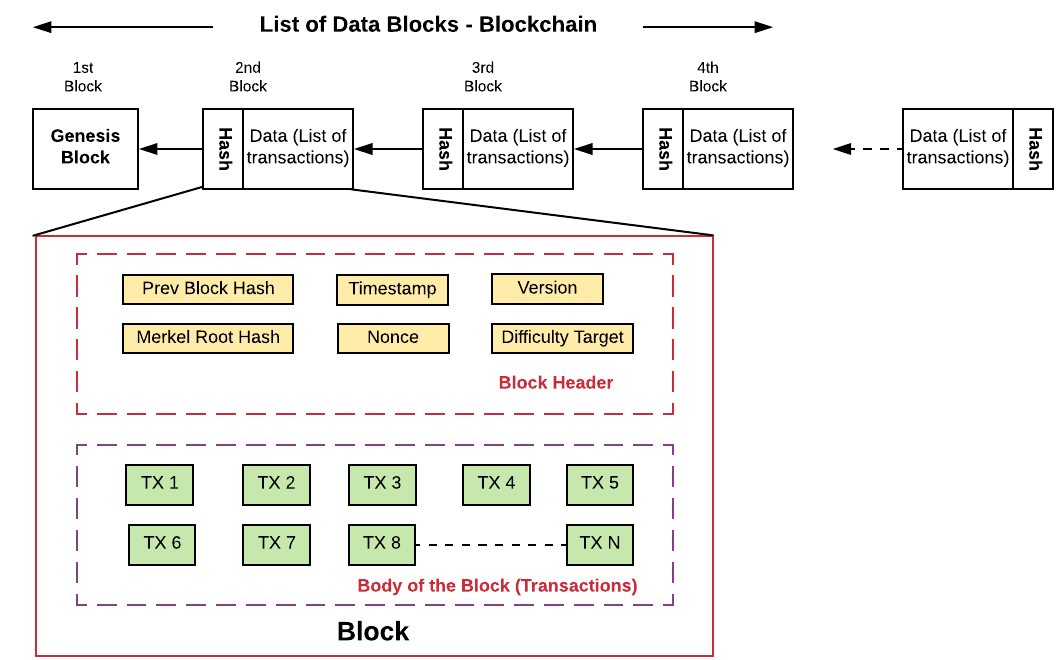
What is the purpose of a blockchain node?
A blockchain exists out of blocks of data. These blocks of data are stored on nodes (compare it to small servers). Nodes can be any kind of device (mostly computers, laptops or even bigger servers). Nodes form the infrastructure of a blockchain.
All nodes on a blockchain are connected to each other and they constantly exchange the latest blockchain data with each other so all nodes stay up to date. They store, spread and preserve the blockchain data, so theoretically a blockchain exists on nodes.
A full node is basically a device (like a computer) that contains a full copy of the transaction history of the blockchain.
Why does Blockchain need coins or tokens?
Tokens/Coins are used as a medium of exchange between the states. They are digital assets built in to perform a specific function within a blockchain.
When someone does a transaction, there is a change of state, and coins are moved from one address to another address. Apart from that, transactions contain some additional data; this data can be mutated through the change of state. For this reason, blockchains need coins or tokens to incentivize the participants to join their networks.
Explain what do nodes do?
When a miner attempts to add a new block of transactions to the blockchain, it broadcasts the block to all the nodes on the network. Based on the block’s legitimacy (validity of signature and transactions), nodes can accept or reject the block. When a node accepts a new block of transactions, it saves and stores it on top of the rest of the blocks it already has stored. In short, here is what nodes do:
- Nodes check if a block of transactions is valid and accept or reject it.
- Nodes save and store blocks of transactions (storing blockchain transaction history).
- Nodes broadcast and spread this transaction history to other nodes that may need to synchronize with the blockchain (need to be updated on transaction history).
Explain why a blockchain needs tokens to operate
Coins/tokens are used to implement changes between states. When somebody does a transaction, this is a change of state, and coins are moved from one address to another. Apart from that, transactions can contain additional data, and a change of state is used to mutate data—the only way to do this in an immutable-by-definition blockchain.
Technically, a blockchain doesn’t need coins for its essential operations, but without them, some other way needs to be introduced to manage states of the chain and to verify transactions.
Explain why there is a fixed supply of bitcoins?
There is a fixed supply of bitcoins. There will never be more than 21 million bitcoins. Bitcoins are created each time a user discovers a new block. The rate of block creation is adjusted every 2016 blocks to aim for a constant two week adjustment period (equivalent to 6 per hour).
The number of bitcoins generated per block is set to decrease geometrically, with a 50% reduction every 210,000 blocks, or approximately four years. The result is that the number of bitcoins in existence will not exceed slightly less than 21 million.
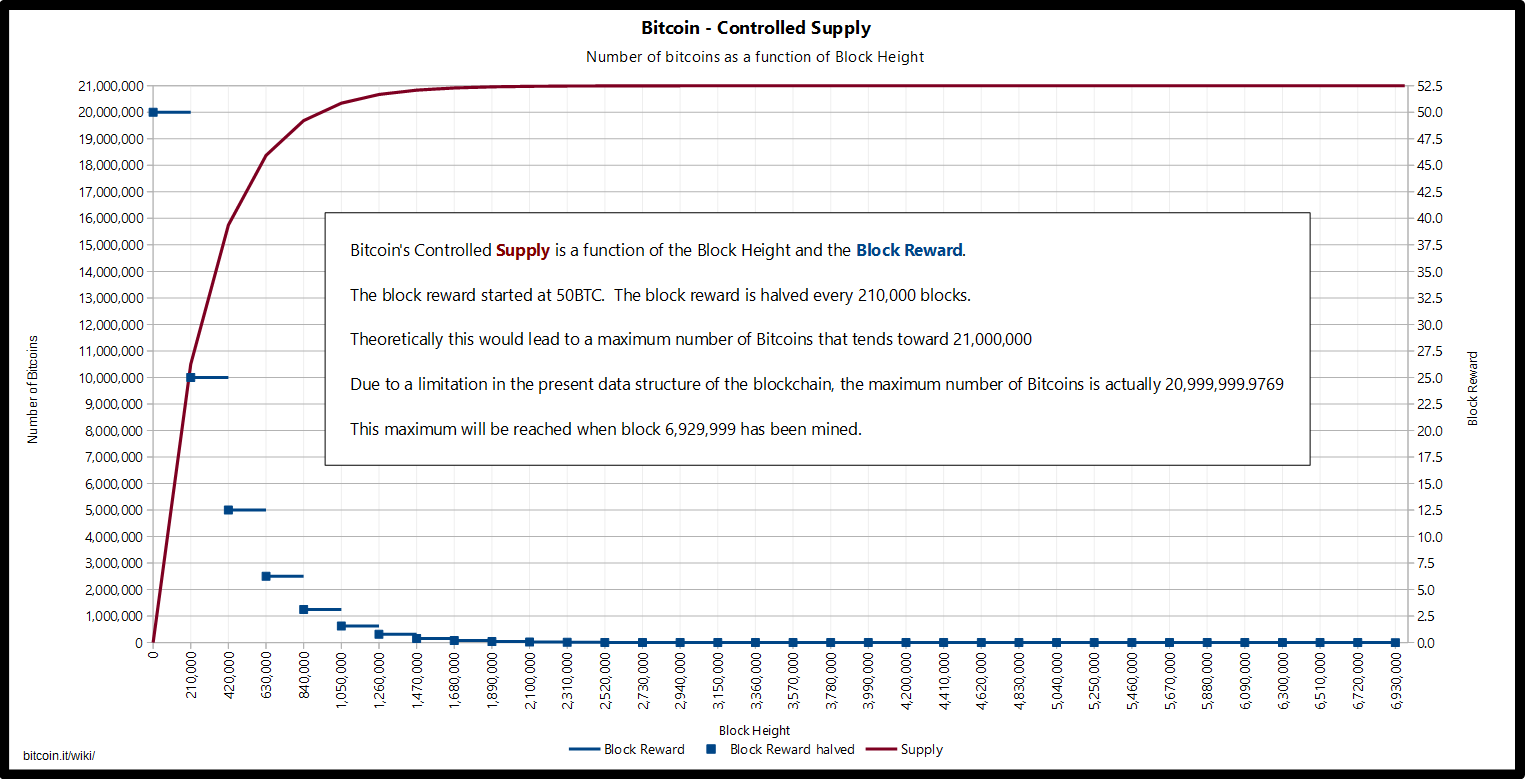
How do verifiers check if a block is valid?
Every full node on the network does block verification. When a new block is announced, every node that receives it does a list of checks. The two most important checks are of proof of work (if a block provides enough work to be included into chain) and of the validity of all transactions (each transaction must be valid).
What are some advantages of using Merke Trees?
Using a Merkle tree can significantly reduce the amount of data that a trusted authority has to maintain for verification purposes. It separates the validation of the data from the data itself.
Merkle trees have three major benefits:
- They provide a means to prove the integrity and validity of data
- They require little memory or disk space as the proofs are computationally easy and fast
- Their proofs and management only require tiny amounts of information to be transmitted across networks
The ability to prove that a log is complete and consistent is essential to blockchain technology and the general ledger concept. Merkle trees help verify that later versions of a log include everything from an earlier version and that all data is recorded and presented in chronological order.
What is DApp or Decentralised Application?
A decentralized application (DApp, dApp, Dapp, or dapp) is a computer application that runs on a distributed computing system.
Decentralized applications don‘t necessarily need to run on top of a blockchain network. Tor, BitTorrent, Popcorn Time, BitMessage, are examples for decentralized applications that run on a P2P network, but not on a blockchain – which is a special kind of P2P network.
DApps have been mostly popularized by distributed ledger technologies (DLT), namely the Ethereum Blockchain, where DApps are often referred to as smart contracts. Its backend code runs on a decentralized peer-to-peer network, and all records of the applicationʼs operation are stored on a blockchain. In most cases, the entire code base is Open Source.
What is Merkle Trees?
Merkle trees are a fundamental part of blockchain technology. A merkle tree is a structure that allows for efficient and secure verification of content in a large body of data.
A Merkle tree summarizes all the transactions in a block by producing a digital fingerprint of the entire set of transactions, thereby enabling a user to verify whether or not a transaction is included in a block.
Merkle trees are created by repeatedly hashing pairs of nodes until there is only one hash left (this hash is called the Root Hash, or the Merkle Root). They are constructed from the bottom up, from hashes of individual transactions (known as Transaction IDs). Hashing is usually conducted using the SHA-2 cryptographic hash function, though other functions can also be used.
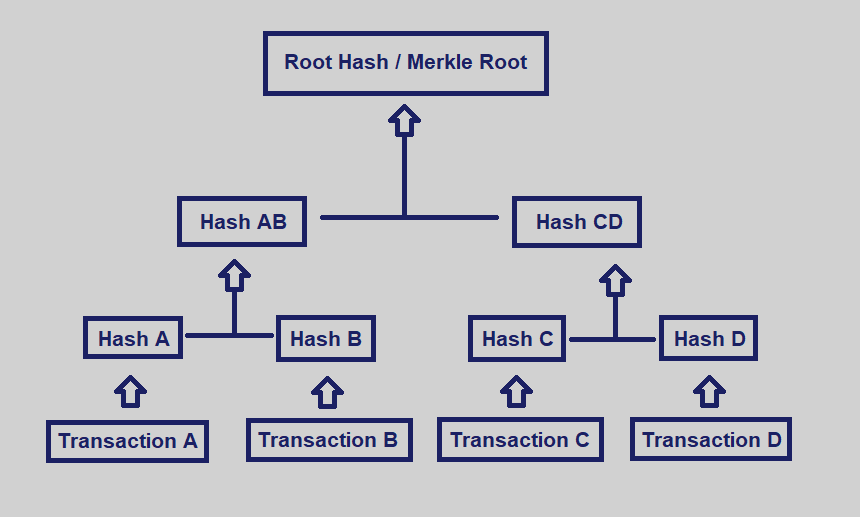
What is RSA algorithm?
RSA (Rivest–Shamir–Adleman) is an algorithm used by modern computers to encrypt and decrypt messages. It is an asymmetric cryptographic algorithm. Asymmetric means that there are two different keys. This is also called public key cryptography, because one of the keys can be given to anyone. The other key must be kept private. The algorithm is based on the fact that finding the factors of a large composite number is difficult.
RSA involves a public key and private key. The public key can be known to everyone; it is used to encrypt messages. Messages encrypted using the public key can only be decrypted with the private key.
What is a smart contract?
A smart contract is a computer protocol intended to digitally facilitate, verify, or enforce the negotiation or performance of a contract. Smart contracts allow the performance of credible transactions without third parties. These transactions are trackable and irreversible.
The aim of smart contracts is to provide security that is superior to traditional contract law and to reduce other transaction costs associated with contracting. Various cryptocurrencies have implemented types of smart contracts.
What is a trapdoor function, and why is it needed in blockchain development?
A trapdoor function is a function that is easy to compute in one direction but difficult to compute in the opposite direction unless you have special information. Trapdoor functions are essential for public key encryption—that’s why they are commonly used in blockchain development to represent the ideas of addresses and private keys.
What is mining difficulty?
Mining difficulty is the degree that determines how hard it is for miners in terms of hashing power (and thus also time) to find an eligible hash aka signature for their block (a block of transactions needs an eligible hash to be verified and added to the blockchain). On the Bitcoin blockchain, miners try to find an eligible hash by hashing random numbers.
A block of transactions will only be accepted by the rest of the network if it has a signature (hash) that meets certain requirements (in example of Bitcoin, the signature needs to start with a certain number of zeroes). In order to find this signature, miners are spending computational power (hashing power) to perform a set of pre-determined operations on random numbers untill they find a number that leads to an output number that meets the requirements.
Finding an output that starts with only one zero is much easier (generally more common) than finding an output number that starts with five consecutive zeroes (this is pretty rare so it would take much more time to find a number that leads to such output).
For example block 100 (back in 2009) only required a signature that started with eight consecutive zeroes, whereas the last recent block (block 542865) needed a signature that started with at least 18 consecutive zeroes.
Why is the blockchain immutable?
Altering a single block requires a new signature for every other block that comes after it all the way to the end of the chain. This is considered to be near impossible. Why?
Let’s say a corrupt miner has altered a block of transactions and is now trying to calculate new signatures for the subsequent blocks in order to have the rest of the network accept his change. The problem for him is, the rest of the network is also calculating new signatures for new blocks. The corrupt miner will have to calculate new signatures for these blocks too as they are being added to the end of the chain. After all, he needs to keep all of the blocks linked, including the new ones constantly being added. Unless the miner has more computational power than the rest of the network combined, he will never catch up with the rest of the network finding signatures.
Millions of users are mining on the blockchain, and therefore it can be assumed that a single bad actor or entity on the network will never have more computational power than the rest of the network combined, meaning the network will never accept any changes on the blockchain, making the blockchain immutable.
Explain what is target hash?
Join FullStack.Cafe to open this Answer. It’s Free! Get Free Access To AnswerJoin 120k+ Developer Who Trust FullStack.Cafe
What is a 51% attack?
Join FullStack.Cafe to open this Answer. It’s Free! Get Free Access To AnswerJoin 120k+ Developer Who Trust FullStack.Cafe
What is a stealth address?
Join FullStack.Cafe to open this Answer. It’s Free! Get Free Access To AnswerJoin 120k+ Developer Who Trust FullStack.Cafe
What is off-chain transaction?
Join FullStack.Cafe to open this Answer. It’s Free! Get Free Access To AnswerJoin 120k+ Developer Who Trust FullStack.Cafe
What is the difference between PoW and PoS?
Join FullStack.Cafe to open this Answer. It’s Free! Get Free Access To AnswerJoin 120k+ Developer Who Trust FullStack.Cafe
Is it possible to brute force bitcoin address creation in order to steal money?
Unlock FullStack.Cafe to open all answers and get your next figure job offer!Share this blog post to open Expert question!
What are miners really solving?
Unlock FullStack.Cafe to open all answers and get your next figure job offer!Share this blog post to open Expert question!
Why is Git not considered a “block chain”?
Unlock FullStack.Cafe to open all answers and get your next figure job offer!
Your Team FREE eLEARNING Courses (Click Here)
Job Opportunities in Blockchain
Job Interview Questions
- Blockchain Jon Interview Question
- Blockchain Interview Question Answer
- Blockchain Interview Question
- Top 29 Blockchain Interview Question
- Blockchain Interview Question
- Blockchain Interview Question with Ans
- Top 7 Blockchain Projects
- Top Promising Blockchain Projects
- Top 17 Blockchain Interview Question
- 34 Blockchain Application, use cases
- Growing List of Blockchain Applications
Related Courses
- Blockchain Programming Course
- Bitcoin, Blockchain, Cryptocurrencies Diploma Course
- Blockchain Training
- Blockchain Technology and APP
- Ethereum Developer
- Blockchain Specialization


